
Hello Friends…
Today’s blog post is about a challenge created by MobileHackingLab. The challenge is called “Food Store.” The goal is to exploit a SQL injection vulnerability and gain elevated privileges within the application.
Lab: https://www.mobilehackinglab.com/course/lab-food-store
When we open the application, we can see two buttons. a login button and a signup button. Firstly, create a new user and log in to the account to see what we can access.
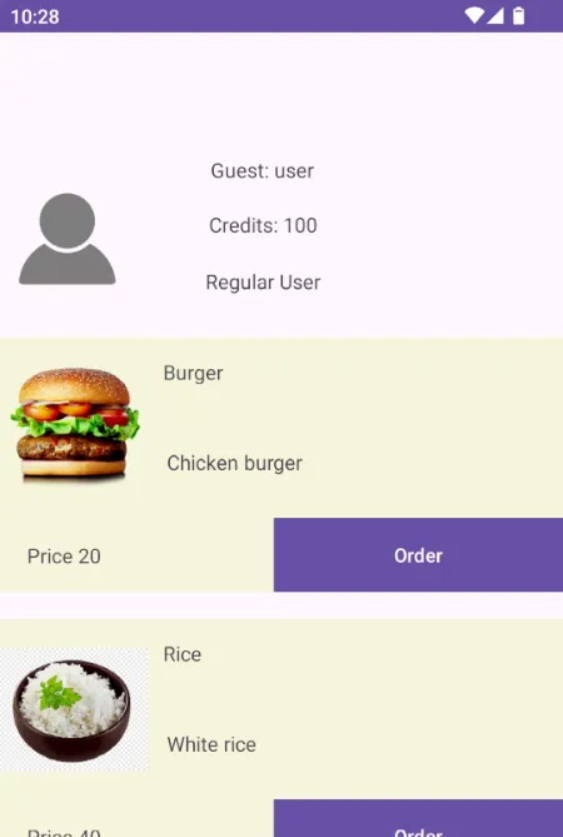
From the screenshot above, you can see the user we registered is a regular user, and the credit is $100. The challenge is to create a pro-user by exploiting the SQLi vulnerability.
Let’s open the APK file in Jadx and analyze the code. We can first check the LoginActivity class.
public static final void onCreate$lambda$1(EditText $usernameEditText, EditText $passwordEditText, LoginActivity this$0, View it) {
Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(this$0, "this$0");
String inputUsername = $usernameEditText.getText().toString();
String inputPassword = $passwordEditText.getText().toString();
User user = this$0.getDbHelper().getUserByUsername(inputUsername);
if (user == null || !Intrinsics.areEqual(user.getPassword(), inputPassword)) {
Toast.makeText(this$0, "Invalid Credentials", 0).show();
return;
}
Toast.makeText(this$0, "Login Successful", 0).show();
int credit = user.isPro() ? 10000 : 100;
Intent intent = new Intent(this$0, MainActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("USERNAME", inputUsername);
intent.putExtra("USER_CREDIT", credit);
intent.putExtra("IS_PRO_USER", user.isPro());
intent.putExtra("USER_ADDRESS", user.getAddress());
this$0.startActivity(intent);
this$0.finish();
}
/* JADX INFO: Access modifiers changed from: private */
public static final void onCreate$lambda$2(LoginActivity this$0, View it) {
Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(this$0, "this$0");
Intent intent = new Intent(this$0, Signup.class);
this$0.startActivity(intent);
}
}
Here, you can see there are two lambda functions. The first function handles the click event for the login button. It retrieves the “username” and “password” entered into the EditText fields. Then it retrieves the user from the database using the “getUserByUsername” method of the “DBhelper” class. If the username and password match, it displays a “Login Successful” toast message and launches the MainActivity. If the added user is a pro, the user credit will be $10,000, and for the regular user, it will be $100. If the username and password do not match, it displays the “Invalid Credentials” toast message.
The lambda2 handles the click event of the signup button. It creates an intent for the signup activity and starts the activity using “startActivity()”.
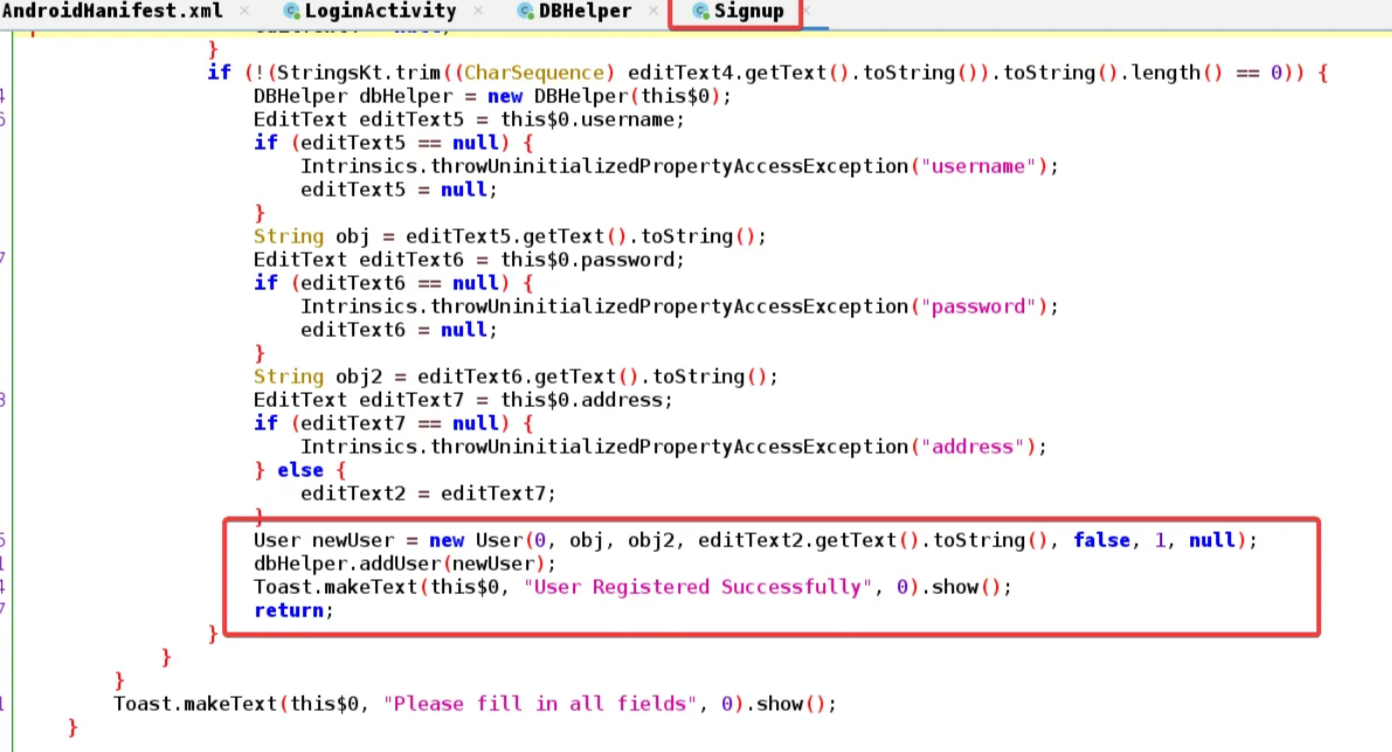
The Signup Activity checks whether the input fields are null or not, creates user objects, and passes them to the “addUser()” method of the “DBHelper” class. This method is responsible for adding the user to the database. The addUser() method likely inserts the user’s information into the database table.
Now let’s analyze the DBhelper class. The DBhelper is used to manage the creation and updating of an SQLite database in an Android application.
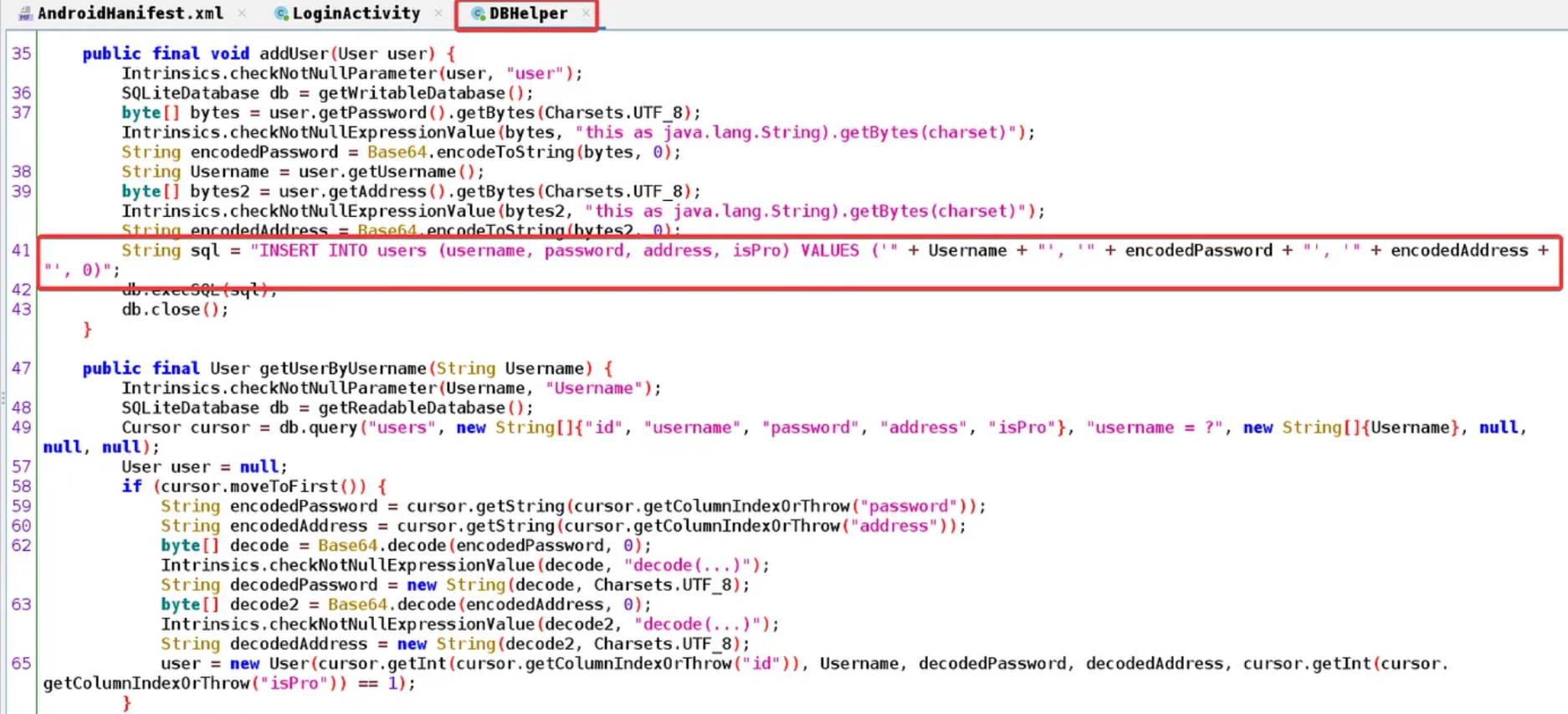
The addUser() method takes a user object as a parameter and adds it to the users table in the database. After that, it encodes the user’s password and address using Base64. Then, it creates an SQL INSERT statement with the user’s information and executes it using execSQL().
The getUserByUsername() method takes a username as a parameter and returns the User object with the matching username from the users table in the database. It queries the “users” table using the provided username and retrieves the corresponding user’s information.
Here, adduser() constructs an SQL query by concatenating strings with user-provided data without any validation, which can lead to an SQL injection attack.
Exploitation
To exploit this vulnerability, all we need to do is create a user with our payload in the username field and some random values in the password and address fields.
Payload used:
attacker','NjY2Ng==','NjY2Ng==', 1);--";
“attacker” is the username, and “NjY2Ng==” is the Base64 encoded form of 6666. I choose 6666 as the password and address, and 1 is the value for “isPro,” indicating that the user is a “pro user.”
The SQL query inside the addUser() will be like;
"INSERT INTO users (username, password, address, isPro) VALUES ('"attacker','NjY2Ng==','NjY2Ng==', 1);--"; + "', '" + encodedPassword + "', '" + encodedAddress + "', 0)";
Open the application and click on the “Signup” button. Fill in the required fields, including our payload, and click on “signup.” Observe that the “user registered successfully” message pops up.
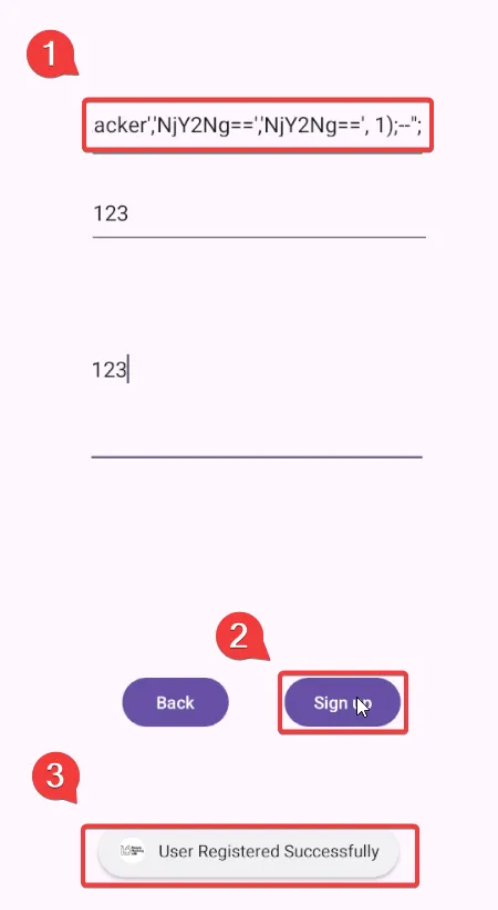
Log into the application using the credentials provided in the payload. Observe that the user (attacker) is added as a Pro user.
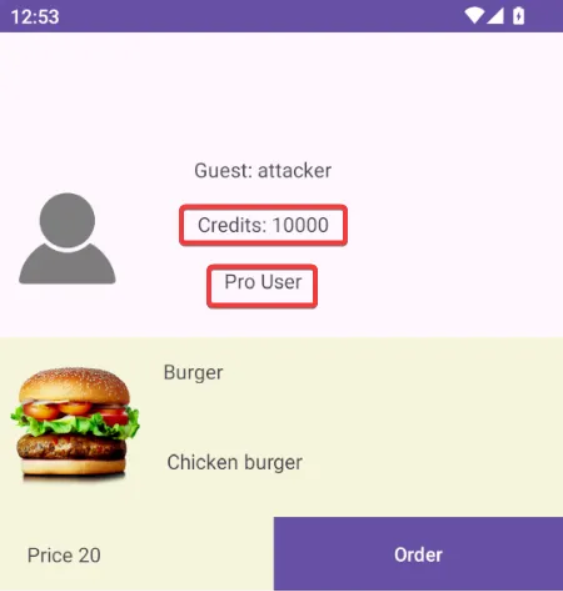
And that’s it; the challenge has been completed successfully.
Completion Certificate:

The MobileHackingLab is an excellent platform for learning and testing your skills. It is recommended for everyone who wants to improve their mobile hacking skills. They provide a range of free labs, and after finishing each challenge, you get a certificate.
Happy Pentesting..!